Dairy Cooling Process and Explanation
In the dairy cooling process, maintaining cool constant temperatures is vital for keeping dairy quality high, and bacteria growth low. Dairy cooling of any kind, including but not limited to cheese, ice cream or frozen yogurt starts off with a main ingredient, milk. Each of these food processes has its own unique technique and series of steps to create its product. Milk, as well has certain methods and phases it must go through before being shipped off as an ingredient.
Raw milk, leaving a cows body is 102°F, can be cooled two ways. These processes are called direct cooling and indirect cooling. The temperatures for milk remains the same, even under different processes. Raw milk must be cooled to 50°F or less within 4 or less of the 1st milking. This allows for pasteurization to occur. Milk must be cooled to 45°F or less within 2 hours after completion of milking. Milk must not succeed 50°F after blending of milk. These constant temperatures are crucial to maintaining health regulations and profits. Temperatures can vary from state to state, but only gradient.
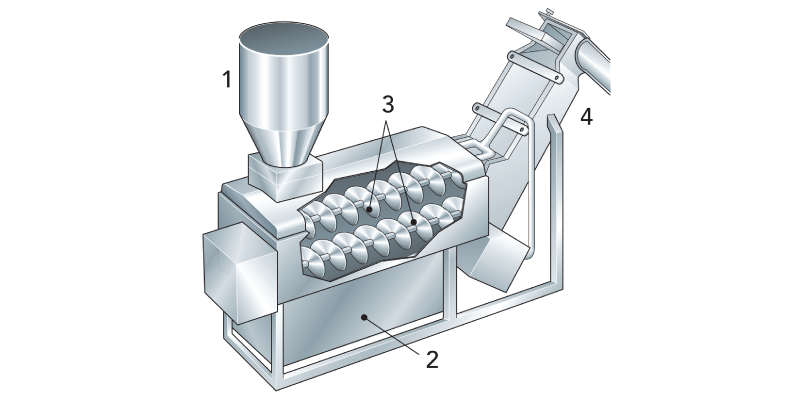
Direct cooling, or direct expansion uses evaporator plates that are used in the lower portion of the storage tank and have direct contact with milk. The evaporator boils liquid refrigerant at a low pressure and temperature. This allows heat from the surrounding space to be absorbed. To keep milk from freezing due to the evaporator agitators are used to keep the milk moving. To much agitation can harm the milk inside the tank. The process of cooling milk must have time to catch up. This technique is used with smaller farms.
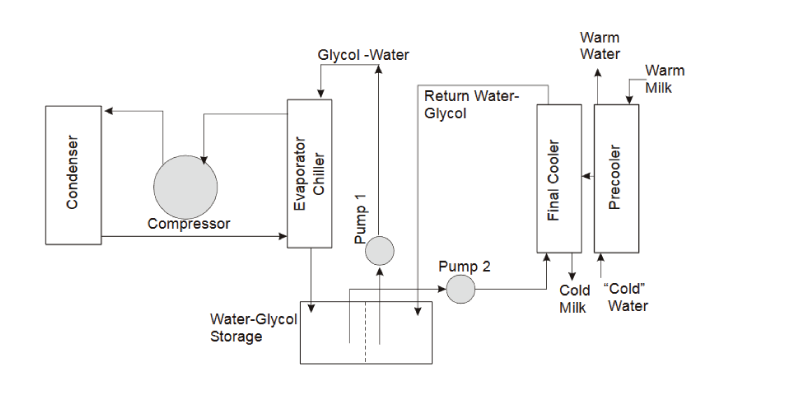
Instant cooling, or indirect cooling cools milk in an external storage tank. The cooling fluid (water, or glycol water mix) comes from a chiller or cooling tower, to chill milk. The cooling occurs in a heat exchanger instead of an evaporator in a tank. The heat exchanger can be as big or as small as a milk production organization needs.
 Packaged Chillers Non-expandable (integrated pump tank) 1.5Ton – 20Ton Single / Dual Circuits Single / Dual Pumps |
 SAE Series Modular Chillers Expandable (pump & tank on separate skid) 1.5Ton – 200Ton Single / Dual Circuits |
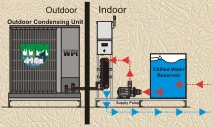 SAR Series Split Chillers Expandable (Outdoor Condensing Unit) (pump, tank, evaporator on indoor skid) 1.5Ton – 200Ton Single / Dual Circuits |