Produce Cooling and Freezing Information
Produce, vegetables and fruits, are subject to multiples cooling and freezing opportunities in the food process industry. This included the hydro-cooling process, and the freezing of produce for consumption. Each piece of produce has different qualities, and temperatures at which they are frozen and hydro cooled.
Hydro-cooling allows for produce to be immersed in cold water, critical for produce to remain fresh and allowing for them to enter a stage of rest. Once produce is plucked from the hot Earth, they must be immediately cooled with 30°F -45°F water. This process increases the shelf life of produce before it is stored in a cold area or frozen for production. Hydro cooling with water can occur in many different ways. These includes continuous hydro-cooling, immersion hydro cooling, batch hydro cooling and truck hydro cooling. All these processes except immersion cooling use spray nozzles to cool vegetables.
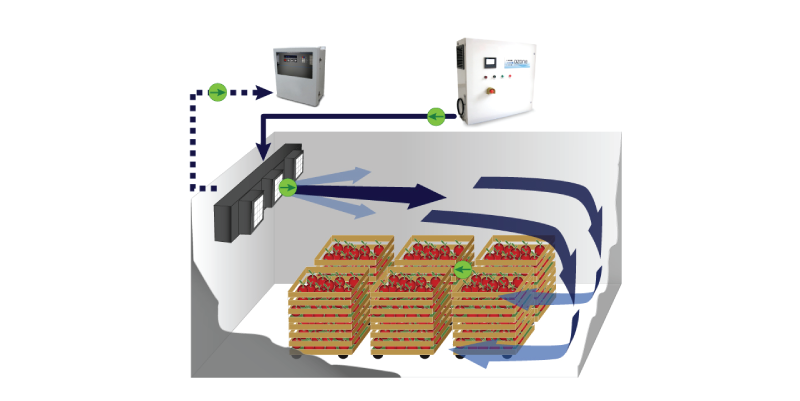
Three main forms of cold storage are forced air cooling, room cooling, vacuum cooling, and evaporative cooling. Room cooling holds produce in a cold room in stacked, vented containers. In order for room storage to work, cooled air must continuously travel of all surface area of the produce. Forced air cooling can occur in tunnels, serpentines, and cold walls. Each of these cooling processes use forced air through fans to circulate around the hot produce. Evaporative cooling is most effective when humidity is low. The water used moves from liquid to vapors. Vacuum cooling is best used on leafy greens. It uses a cooling chamber.
After the vegetables have gone through a post-harvest process, they are then blanched. Blanching, which occurs in dipping vegetables in boiling hot water for a few minutes, kills enzymes that affect the taste, color, and shrining of vegetables. The produce is then sorted and sent to a brine cooling station. Peas can be frozen and then packed or vice versa. Peas can be frozen via blast tunnel. Or, they can be cooled by horizontal/vertical cooling. If they are packed before cooling, they can be loaded in boxes and be plate freezed.